Unlocking Wellness: The Power of the Brain-Gut Connection and Healthy Eating
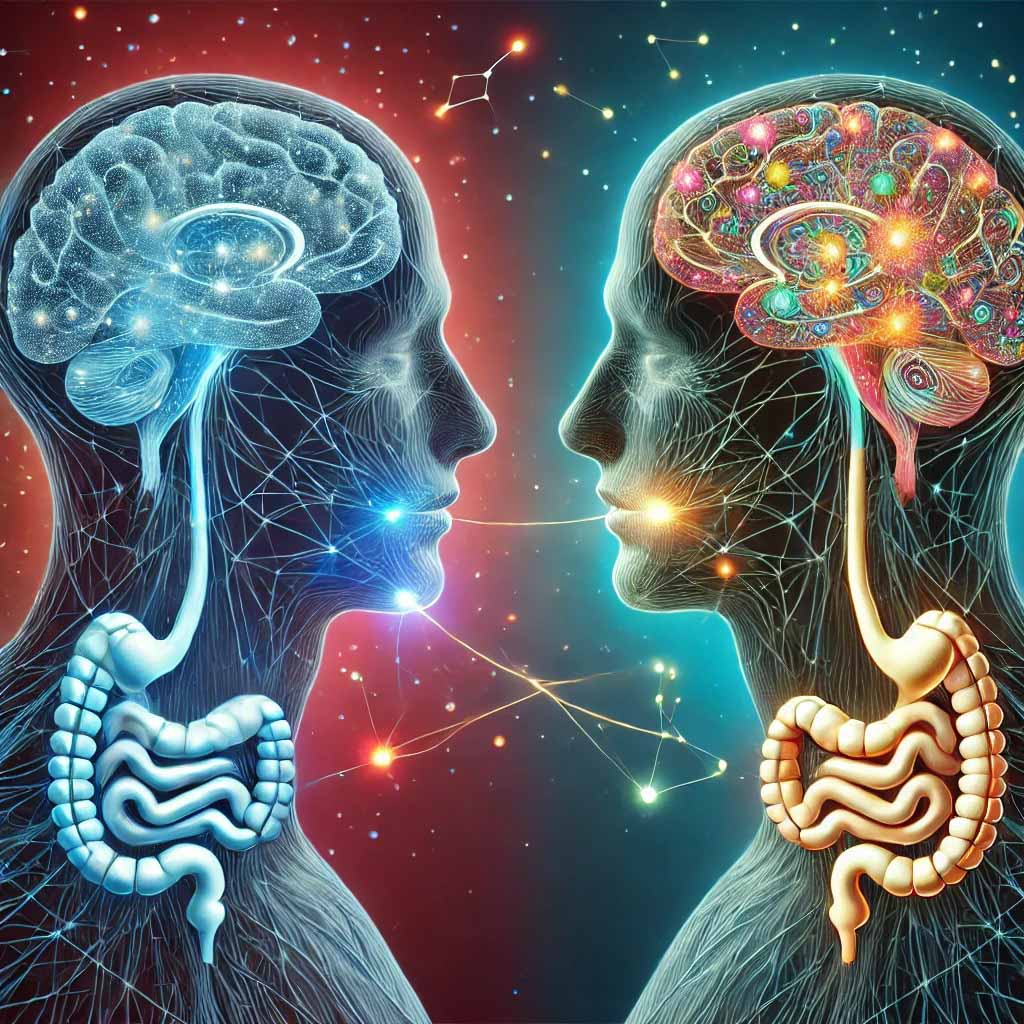
The Brain-Gut Connection: Understanding the Impact of Diet on Mental and Physical Health
Have you ever wondered how the food you eat affects not just your body, but your mind and emotions? Imagine a world where your dietary choices can influence your mood, your thoughts, and even your behaviors. What if you could unlock a path to better mental health simply by understanding the intricate connection between your brain and gut?
Recent research has illuminated the fascinating ways in which our gut microbiota can shape our emotions and cognitive functions. Let’s embark on a journey to explore the brain-gut connection, the dangers of bad eating habits, and the six remarkable benefits of eating healthier.
The Brain-Gut Connection
The connection between the brain and the gut is a vital area of study in understanding how diet affects our overall health. This relationship, often referred to as the “gut-brain axis,” involves a complex communication system that impacts our emotions, behaviors, and cognitive functions.
- Influence of Gut Microbiota on Behavior: Research has shown that gut bacteria can significantly influence behavior. In experiments, transferring gut bacteria from anxious mice to calm mice resulted in the calm mice displaying anxiety-like behaviors, and vice versa. This indicates that our gut microbiota play a crucial role in shaping our emotional responses.
- Human Studies on Gut-Brain Axis: Studies in humans have also demonstrated the impact of gut microbiota on psychological well-being. For example, consuming B-GOS prebiotics has been shown to lower waking cortisol levels, a marker of stress, and improve emotional processing in ways similar to anti-anxiety medications. This highlights the potential of dietary interventions in managing stress and improving mental health.
- Diet’s Impact on Psychological Symptoms: A healthy diet, particularly one rich in vegetables and low in sugar and processed foods, can protect against depression. A long-term study involving 15,000 adults in Spain found that those who adhered to a healthy diet were less likely to develop depression over ten years. This underscores the importance of dietary choices in maintaining mental health.
- Early Life Stress and Gut Microbiota: Stress experienced during early pregnancy can disrupt the microbiome of the developing infant, leading to long-term psychological effects. Additionally, early life trauma can alter gut microbiota and brain structure, increasing anxiety-like behaviors and sensitivity to gut stimuli. This highlights the significance of maintaining gut health from an early age to promote psychological well-being.
Dangers of Bad Eating Habits
Consider the potential pitfalls of your current eating habits. How might these be undermining your mental and physical health? Let’s delve into the hazards associated with poor dietary choices.
- Increased Risk of Depression: Picture the impact of a diet loaded with processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats. Diets like these are often linked to higher rates of
 depression. Avoiding such foods could prevent negative effects on your brain function and mood regulation.
depression. Avoiding such foods could prevent negative effects on your brain function and mood regulation. - Cognitive Decline: Reflect on your daily food intake. An unhealthy diet can speed up brain aging, causing brain atrophy, particularly in the hippocampus, which is crucial for memory and learning. Taking steps to eliminate unhealthy foods could protect your cognitive health.
- Increased Stress and Anxiety: Think about your stress levels. Diets that lack essential nutrients can amplify stress and anxiety. For instance, high sugar consumption can lead to fluctuations in blood glucose levels, causing mood swings. Avoiding high sugar foods could help you manage stress more effectively.
- Digestive Issues: Contemplate your gut health. Poor dietary habits can lead to conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), negatively impacting both your physical and mental health. Making dietary changes to avoid unhealthy foods could improve your gut health and overall mental well-being.
Six Benefits of Eating Healthier
Imagine a life where you feel energized, happy, and mentally sharp. Here are six benefits of eating healthier:
- Longevity: Healthy eating, especially diets high in vitamins and minerals, is positively associated with living a longer life. People who eat healthily are less likely to suffer from diseases like heart disease that can cause long-term health issues or premature death. Longevity is not associated with specific fad diets but rather with following basic nutrition principles (Åhlberg, 2021; Lim, 2018).
- Lower Risk of Chronic Diseases: Eating a healthy diet is associated with a lower risk of heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. If you are worried about a family history of these diseases, incorporating healthy eating into your lifestyle can be beneficial (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2022).
- Healthy Immune Function: A diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can help your immune system function better. As we age, our immune function decreases, but eating plenty of fruits and vegetables can help our bodies fight disease (Calder, 2022).
- Healthier Pregnancies: Eating a healthy diet during pregnancy can promote brain development and healthy birth weight for babies, while reducing risks to the mother such as anemia, fatigue, and morning sickness (National Institutes of Health, 2022; Allen, 2000).
- Strong Bones: A healthy diet contributes to strong bones, which is important for children whose bones are growing and for adults to avoid conditions like osteoporosis. Strong bones improve overall wellness and ease daily activities (Abrams, 2021).
- Improved Mental Health: There is a strong association between poor nutrition and disorders like anxiety and depression. Improving your diet can benefit your mental health by providing the necessary nutrients that support brain function and emotional well-being (Adan et al., 2019).
Conclusion
Understanding the brain-gut connection and the impact of diet on mental and physical health underscores the importance of healthy eating habits. By adopting a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, you can enhance your emotional well-being, cognitive function, and overall quality of life.
Why not start making mindful food choices today? Nourish your body, support a healthier mind, and unlock a path to better mental health.
Ready to take the first step towards better health? Try incorporating one healthy food into your diet this week.
Share your journey with us in the comments! 🌟
Don’t forget to subscribe to our blog for more insights into health and well-being. Follow us on social media for daily tips and inspiration. Let’s embrace a healthier lifestyle together! 💪🍎
References
- Abrams, S. A. (2021). Bone Health in School Age Children: Effects of Nutritional Intake on Outcomes. Frontiers in nutrition, 8, 773425.
- Adan, R. A., van der Beek, E. M., Buitelaar, J. K., Cryan, J. F., Hebebrand, J., Higgs, S., … & Dickson, S. L. (2019). Nutritional psychiatry: Towards improving mental health by what you eat. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 29(12), 1321-1332.
- Åhlberg, M. K. (2021). A profound explanation of why eating green (wild) edible plants promote health and longevity. Food frontiers, 2(3), 240-267.
- Allen, L. H. (2000). Anemia and iron deficiency: Effects on pregnancy outcome.
- Calder, P. C. (2022). Foods to deliver immune-supporting nutrients. Current Opinion in Food Science, 43, 136-145.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention-Nutrition (2022).
- Lim, S. (2018). Eating a Balanced Diet: A Healthy Life through a Balanced Diet in the Age of Longevity. Journal of obesity & metabolic syndrome, 27(1), 39–45.
- National Institutes of Health (2022).
Sajid Ahamed is a “Certified Trainer of NLP” and organizes John Grinder approved New Code NLP and NLP Master Practitioner Certifications Courses in India and the Middle East. He has more than 1000 hours of coaching experience and is an ICF accredited Professional Certified Coach (PCC). Apart from the Trainings, he covers a wide niche of coaching including Relationship Coaching, Parenting Coaching, Leadership Coaching.
To be updated with latest trends in Coaching and psychotherapy, join our Facebook Private Group.
For Further networking, follow us on Facebook | Instagram | Youtube